SDLC or Software Development Life Cycle is a blueprint for creating a software application. It’s a clear step-by-step process to build software.
The Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) provides a structured framework for developing high-quality software efficiently and effectively. SDLC ensures a systematic approach to transforming ideas into tangible solutions, guiding teams through well-defined phases such as planning, design, development, and maintenance. For businesses, adhering to SDLC means minimizing risks, improving project timelines, and delivering software that aligns with their goals.
Software development life cycle adherence is one of the major factors that you need to look at while selecting the most appropriate software development company.
In this blog, we will discuss everything you need to know about the Software Development Life Cycle and show a few benefits of adopting it.
Table of Contents
Benefits of Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC)
Software Development Life Cycle provides a wide range of advantages to businesses. Whether it is startup or an established firm, the benefits of hiring software developers are immense. We have mentioned below the most important advantages that SDLC provides to the development teams.
Clarity in goal-setting
Best Software Developers clearly knows the goals they need to meet and the deliverables they must achieve by a set timeline, lowering the risk of time and resources being wasted.
Proper testing
The software development life cycle models will implement the necessary checks and balances to ensure that the software is thoroughly tested before release.
Clear stage progression
With an SDLC, developers are unable to progress to the next stage until the previous one is completed. You’ll be able to see a clear succession of stages this way.
Member flexibility
Since the SDLC process steps have well-structured documents, the dedicated software development team can replace the team members that have left the team seamlessly.
Perfection is achievable
The SDLC stages are designed in a way that they create a feedback loop. Thus, through a proper software product development process, you can iterate and improve upon the projects over and over until they are perfect.
Software Development Life Cycle: Phases Explained for Business Success
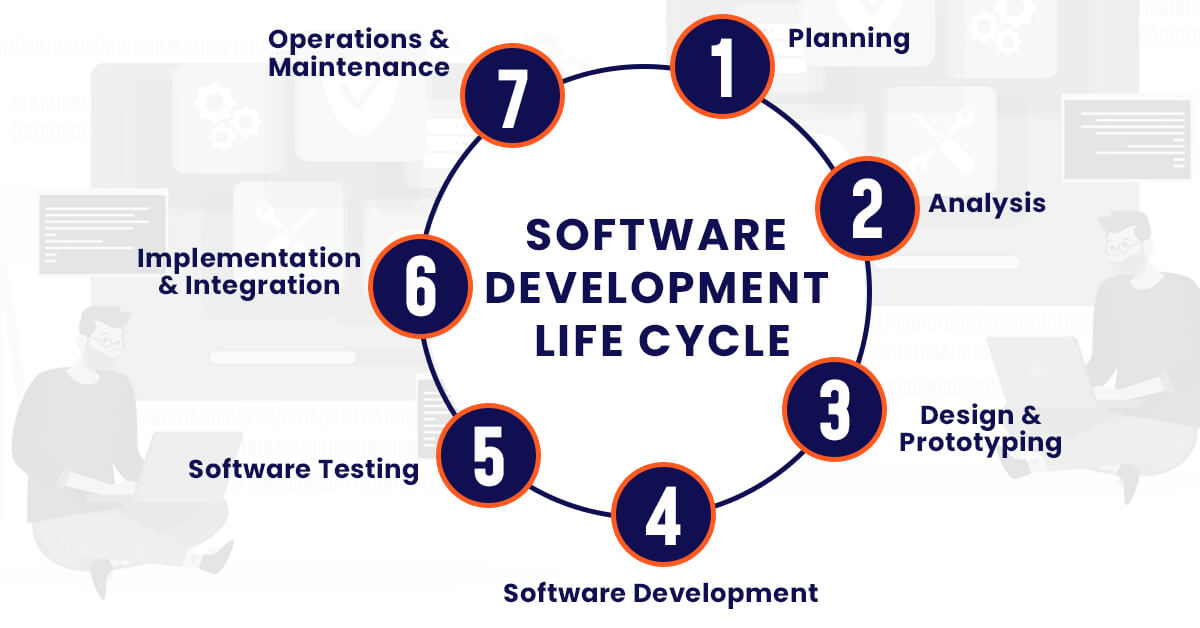
The software development life cycle typically has 7 stages of software development. Here’s a brief breakdown of the various phases in the life cycle of the Software Development Process.
- Planning stage
- Analysis stage
- Design and prototyping stage
- Software development stage
- Software testing stage
- Implementation and Integration stage
- Operations and maintenance stage
Now let’s take a closer look at each stage individually.
Planning of Software development
The Planning phase is crucial for setting the groundwork for the entire project. It involves defining the project’s scope, objectives, timelines, and identifying the necessary resources. Decision-makers evaluate the feasibility of the project from a technical, operational, and financial perspective.
Example: For an e-commerce platform, the planning phase would involve deciding what features (e.g., payment gateways, product catalogs) need to be developed, the project timeline, and cost estimations for infrastructure and software development teams.
Key Activities:
- Feasibility Study: Assess the project’s viability.
- Resource Allocation: Define the required team, tools, and technologies.
- Risk Management: Identify potential risks and mitigation strategies.
Business Impact: Careful planning ensures that the project starts on the right foot, aligning expectations, minimizing risks, and optimizing resources from the start.
Requirement Analysis for Software development
In the Requirement Analysis phase, business analysts and stakeholders work together to gather and document both functional and non-functional requirements. This phase is critical to understanding what the software must accomplish and how it should perform.
Example: For a banking software development, functional requirements could include features like funds transfer, while non-functional requirements would cover performance expectations such as speed and security.
Key Activities:
- Functional Requirements: Defining features and functionality.
- Non-Functional Requirements: Determining performance, usability, and security needs.
- Requirement Validation: Ensuring all requirements meet the business objectives and technical feasibility.
Business Impact: Accurate and thorough requirement analysis reduces the risk of scope creep or uncontrolled growth and ensures the project meets client expectations from the beginning.
Software Design Process
During the Software Design phase, developers and architects take the requirements and translate them into a blueprint for how the software will look and function. This includes both high-level system architecture and detailed design for each component.
Example: For a healthcare management system development, this phase would involve designing the database to store patient records, the user interface for healthcare providers, and integrating with third-party APIs for lab results.
Key Activities:
- High-Level Design: Defining system architecture and data flows.
- Low-Level Design: Detailed design for each module, database structure, and user interfaces.
- Technology Selection: Choosing the appropriate technologies, frameworks, and databases.
Business Impact: A well-structured design improves efficiency during development and ensures scalability, allowing the software to grow with future business needs.
Software Development and Implementation (Coding)
The Implementation phase is where the actual coding and software development happens. Software developers begin translating the design documents into working software. This phase of the SDLC procedure involves writing code, building the system’s core features, and integrating different modules.
Example: While building a ride-sharing software application, the implementation / software development phase includes developing user-facing features like ride booking, driver tracking, and payment processing, while ensuring that backend components like database interactions and APIs function smoothly.
Key Activities:
- Code Development: Writing and organizing code into functional modules.
- Version Control: Using tools like Git to manage code changes and collaboration.
- Code Review: Conducting peer reviews to ensure quality and compliance with standards.
Business Impact: High-quality coding practices ensure maintainability, scalability, and reduce post-deployment issues in Software, leading to faster product launches and reduced long-term costs.
Software Testing
In the Testing phase of the Software development life cycle, the developed software is rigorously tested to identify and fix any bugs, errors, or issues. Different types of Software testing such as Unit testing, System testing, Performance testing, Integration testing, UAT, White box testing, and Black box testing are conducted to ensure that the software functions correctly under different conditions and meets the original requirements.
Example: For developing an online retail platform, testing would involve ensuring the checkout process works flawlessly, that the site can handle high traffic, and that user data is securely encrypted.
Key Testing Types:
Unit Testing: Testing individual components of Software for correctness.
Integration Testing: Ensuring that different modules work together.
User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Validating that the software meets user needs in a real-world scenario.
Business Impact: Thorough Software testing process improves product reliability, ensures better user experiences, and minimizes the risk of critical failures after deployment.
Deployment of Software
Once the software has passed all testing phases, it is ready for deployment. This SDLC phase involves delivering the software to the production environment, making it available to end-users. Depending on the complexity of the software, deployment can be a single-phase launch or a multi-stage process (e.g., rolling out new features gradually).
Example: In a large financial software, the deployment may begin with a beta launch to a select group of users, followed by a full release once initial user feedback has been gathered and adjustments have been made.
Key Activities:
Beta Testing: A small group of users test the software before the full release.
Go Live: Releasing the software to all users.
Training: Providing user training and support documentation for effective use.
Business Impact: Smooth deployment ensures minimal disruption to operations, with quick adoption of the software, helping businesses to maximize ROI quickly.
Maintenance of Software
Once the software is released, the Maintenance phase begins. This involves monitoring the software’s performance, fixing any bugs that arise post-launch, making necessary updates, and adding new features as needed. Continuous support is essential to keep the software running smoothly and adapting to evolving development trends and business needs.
Example: For a subscription-based streaming service, regular Software maintenance would involve updating the platform with new features, fixing bugs, and ensuring uninterrupted streaming.
Key Activities:
- Bug Fixes: Resolving issues that emerge after Software deployment.
- Updates and Enhancements: Adding new software features based on user feedback or business demands.
- Performance Monitoring: Continuously tracking system performance to ensure it meets benchmarks.
Business Impact: Continuous maintenance prolongs the software’s lifespan, ensures it remains relevant to business needs, and enhances customer satisfaction through ongoing improvements.
Real-World Applications of SDLC
The Software Development Life Cycle is a framework that is widely adopted across various industries to ensure software is developed in a structured, efficient manner. Let’s explore some real-world applications and industries that benefit from SDLC:
Finance
In the finance industry, Software Development Life Cycle is critical for building secure, scalable systems like online banking platforms, fraud detection tools, and payment gateways. Adopting SDLC processes ensures that stringent security protocols are followed, reducing risks and ensuring compliance with financial regulations like PCI-DSS.
Example: Major banks rely on SDLC to develop secure custom software solutions that undergo rigorous testing to safeguard customer data.
Healthcare
Healthcare software, such as Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems and telemedicine platforms, requires strict adherence to SDLC to ensure patient data security, privacy, and compliance with regulations such as HIPAA. The design, development, and testing phases are crucial to prevent system failures that could affect patient care.
Example: Hospitals use SDLC to develop EHR systems that integrate seamlessly with various departments, ensuring reliable access to patient information.
eCommerce
The e-commerce industry uses SDLC to create robust online platforms that handle high transaction volumes and provide a smooth user experience. From payment processing to order management, the Software development process ensures the development of scalable, secure, and high-performance e-commerce systems.
Example: Large retailers use SDLC to build scalable platforms that can handle increased traffic surges during sales events, ensuring reliability and security.
Manufacturing
Manufacturing businesses use software development lifecycle to develop systems that monitor production lines, track inventory, and optimize supply chains. Automation software and predictive maintenance tools, built using the SDLC framework, enhance operational efficiency and reduce downtime.
Example: Factories implement SDLC to design automation systems that prevent equipment breakdowns and improve production flow.
Government and Public Services
Government agencies use SDLC to develop secure portals, databases, and systems that handle citizen data and public services. These systems need to be robust, secure, and able to comply with various regulations, making it an essential part of their development process.
Example: Governments apply SDLC to build tax filing systems, ensuring they are secure, easy to use, and can handle peak filing periods.
Education
Educational institutions use SDLC to create platforms for learning management systems (LMS), online courses, and student management systems. Its proper execution ensures that these platforms are user-friendly, scalable, and capable of handling sensitive student information securely.
Example: Universities use SDLC process to develop LMS platforms that enable distance learning, manage assignments, and track student performance effectively.
SDLC: Closing the Loop
By following these detailed Phases of the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC), businesses can build and deploy reliable software that meets client expectations. Each phase is crucial in minimizing risks, optimizing resources, and delivering high-quality software that adds significant business value. For decision-makers, implementing a structured software development process ensures that their projects remain on track, within budget, and adaptable to evolving business needs.
Each stage of the SDLC is essential for ensuring that software development is efficient, cost-effective, and aligned with the business’s strategic goals. Detailed planning, analysis, and execution throughout these phases help businesses deliver high-quality software that meets or exceeds client expectations, while also ensuring long-term viability through proper maintenance and updates.
Frequently Ask Questions for Assessment of SDLC
What are the development-related environments while following SDLC?
The team of proficient developers follows different environments while using Software System Development Life Cycle. They are-
- Dev
- SIT
- PROD
- UAT
What are the top Software Development Life Cycle tools?
Various system development life cycle tools are leveraged by the topmost and leading software development companies in the world to accomplish more with less and ensure the best results. The trending tools for SDLC are-
- Jira
- Git
- Asana
- Confluence
What do you mean by LLD and HLD in SDLC?
HLD is abbreviated as High-Level Design which provides system design for the database and functional architecture for all the modules and sub-modules. LLD is abbreviated as Low-Level Design that provides the detailed design for modules and programs, including logic for each component and verifying module specifications.
What are the differences Between SDLC And STLC?
STLC is about a Software Testing Life Cycle that’s designed for testing various development phases- planning, design, execution, and release. It’s only about validation to see if data collected from SRS meets the requirements. On the other hand, SDLC aka Software Development Life Cycle is a systematic process of shaping a software idea into a full-fledged solution. all the phases from planning to deployment are validated and analyzed for impeccable delivery.
What are the different software development life cycle methodologies?
There are various SDLC methodologies leveraged worldwide. Here are a few popular methodologies that are used at scale.
- Agile methodology
- Waterfall methodology
- Spiral methodology
- Rapid application development model
- Iterative model
- DevOps model
- Big-bang model
- V-shaped model
- Scrum methodology
- Evolutionary prototype model
 Avantika Shergil
| Oct 22, 2024
Avantika Shergil
| Oct 22, 2024
Avantika Shergil is a technology enthusiast and thought leader with deep expertise in software development and web technologies. With over 8 years of experience analyzing and evaluating cutting-edge digital solutions, Avantika has a knack for demystifying complex tech trends. Her insights into modern programming frameworks, system architecture, and web innovation have empowered businesses to make informed decisions in the ever-evolving tech landscape. Avantika is passionate about bridging the gap between technology and business strategy, helping businesses build customized software and website, and understand about different tools to leverage effectively for their ventures. Explore her work for a unique perspective on the future of digital innovation.